Enhance your Research with ProSci’s Polyclonal Antibody Services
What are Polyclonal Antibodies?
Download the white paper.
Polyclonal antibodies are a mixture of antibodies from multiple B-cell clones of a host animal that can recognize multiple epitopes on an antigen. Their unique binding characteristic to different epitopes can help amplify their signal, leading to increased sensitivity and better detection. Unlike monoclonal antibodies, created by selecting a single B-cell clone, polyclonal antibodies occur naturally through the immune response. Numerous applications, including Western Blot, ELISA, immunohistochemistry, and immunoprecipitation, can be carried out using polyclonal antibodies. Polyclonal antibody therapeutics are also commonly utilized in medicine for virus and toxin neutralization and immunoglobulin replacement therapy (3). In diagnostics, polyclonal antibodies are used for pathology and lateral flow tests, among others.
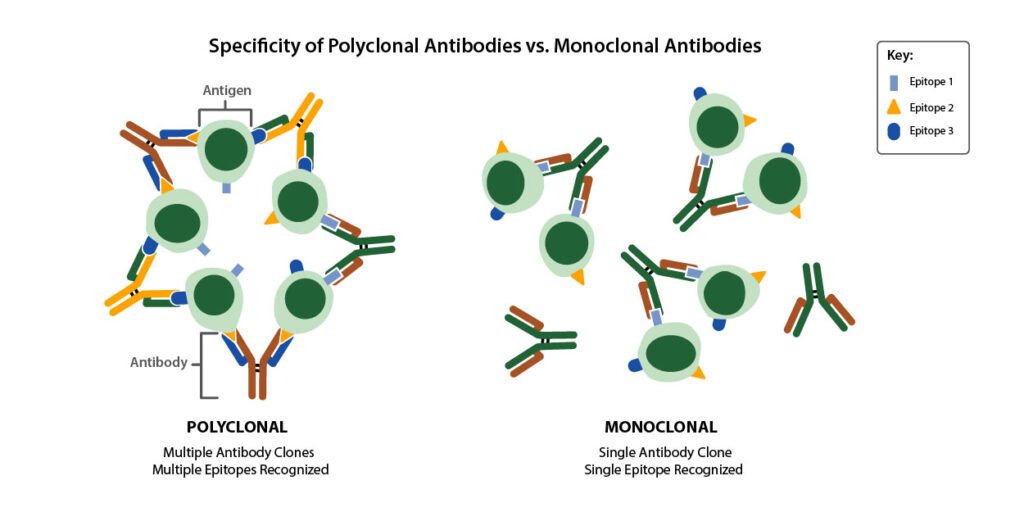
There are known limitations, such as limited supply and off-target binding of these antibodies. New technologies readily overcome these issues, such as stringent validation procedures to maximize lot-to-lot reproducibility. With innovative methods available to overcome the limitations of polyclonal antibodies, they remain excellent cost-effective tools for researchers, diagnostic developers & drug developers alike.
Benefits of Polyclonal Antibodies
- Clonal Properties:
- Due to their ability to detect several target protein epitopes, polyclonal antibodies have a high sensitivity to the target protein.
- Biophysical Diversity:
- Polyclonal antibodies are more stable than other antibodies when environmental factors cause other antibodies’ inactivation, lability, or precipitation.
- Provides researchers with modification opportunities, including:
- Host species
- Antigen quantity
- Amount and distribution of injection sites
- Antigen injection frequency
- Adjuvant type
- Adjuvant quantity
- Quicker Production timeline
- Development and production are done in parallel
- Competitive pricing
Check out the complete catalog of polyclonal antibodies for various applications, from ProSci!
Customize Your Research with Polyclonal Antibody Services!
Our service team can assist you with designing, purifying, and producing custom polyclonal antibodies.
- Expertise in immunogen determination and peptide design
- Isolation of spleen and splenocytes to convert a rabbit polyclonal to monoclonal
- Provision of organs as a deliverable
- Multiple Ph.D. scientists with specialized knowledge and experience
- Exceptional customer service
- Customizable deliverables tailored to meet specific needs
- Custom schedules available to fit any timeline
At ProSci, these antibodies are generated in various host species from customized immunogens designed by expert antibody scientists. Our experts have years of experience designing antigens for small peptides, large proteins, small molecules, and special modifications such as post-translational modifications (PTMs), including phosphorylation and glycosylation. They carefully pair antigen designs to host animals, paying close attention to your desired final application to maximize success. ProSci offers Polyclonal Antibody Services in various custom configurations and standard packages, from Antigen Design and Synthesis to Immunization to Production. See our Polyclonal Antibody Services here.
Does your project require polyclonal antibodies? Our antibody experts and skilled project managers are dedicated to saving you time and costs and optimizing your project to accelerate your next breakthrough. Partner with ProSci and research confidently.Take your discoveries to the next level and enhance your research with ProSci’s polyclonal antibody services today.
Contact us today to discuss your next project!
References
- Bordeaux J, Welsh AW, Agarwal S, et al. Antibody validation. BioTechniques. 2010;48(3):197-209. doi:https://doi.org/10.2144/000113382
- Lipman NS, Jackson LR, Trudel LJ, Weis-Garcia F. Monoclonal Versus Polyclonal Antibodies: Distinguishing Characteristics, Applications, and Information Resources. ILAR Journal. 2005;46(3):258-268. doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.46.3.258
- Pelletier, J. P. R., & Mukhtar, F. (2020). Passive Monoclonal and Polyclonal Antibody Therapies. Immunologic Concepts in Transfusion Medicine, 251–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-67509-3.00016-0
- Wootla, B., Denic, A., & Rodriguez, M. (2014). Polyclonal and monoclonal antibodies in clinic. Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.), 1060, 79–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-62703-586-6_5

